Presenting new benchmarks for measuring valueImpact measurement/management Focus areas
As an organization whose goal is to popularize impact investing and impact-oriented philanthropy in Japan, SIIF is engaged in the practice of, and development of knowledge and nurturing of practitioners for, the impact measurement and management initiatives that constitute the preconditions for such activities. With global interest in building sustainable societies rising steadily, we have arrived at an era in which even companies are being measured not only by economic activity such as profitability, but by the degree of their contribution to society. In addition, there is also a movement among not-for-profit organizations such as NPOs to clarify the degree of their contribution to resolving social problems. The process of making visible the results and changes in society and the environment caused by the activities and services provided by companies and not-for-profit organizations is referred to as “impact measurement.” The process of using information related to social results to improve businesses and to make decisions with the intent of enhancing impacts is referred to as “impact management.”
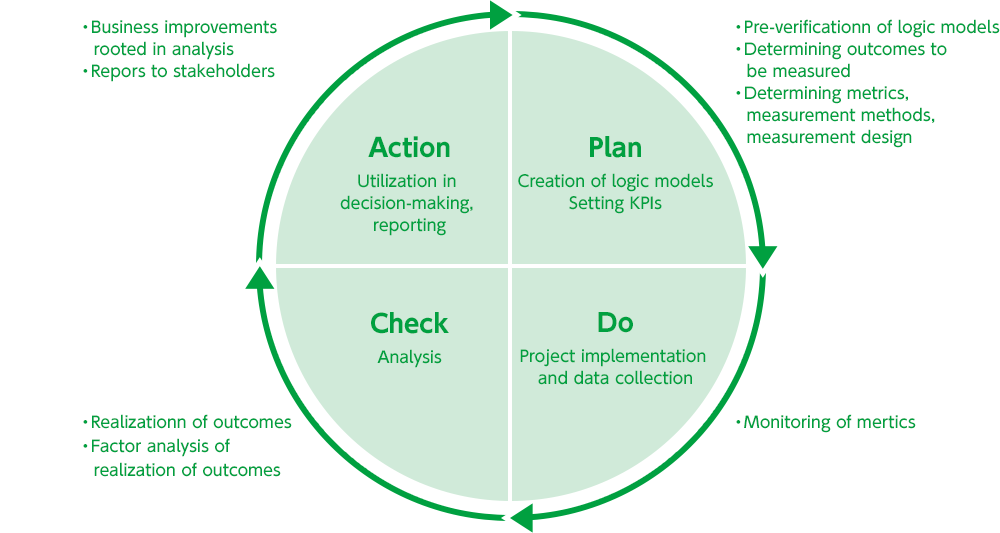
A logic model is a repreentative tool used in impact evaluation and management.
Using a logic model, we regularly monitor the implementation status. The results are analyzed and used for management decision-making, explanation and reporting to stakeholders, and the PDCA cycle is implemented.
Source: IMP, “What is impact?” <https://impactmanagementproject.com/impact-management/what-is-impact/>
SIIF collaborates with national and international organizations that promote impact investment and impact evaluation and management, disseminates the latest trends in Japan and overseas, and works to disseminate knowledge in Japan.
As an international trend, there is a need for a mechanism to “optimize” the social value of projects and activities, to “verify” this value, and to link this to learning and improvement of one’s own organization and activities, and to accountability to funders and others.
出典:SIMI
Overview of activities
What is “Impact measurement/management”?
Impact Measurement & Management
Representative methods for impact evaluation and management
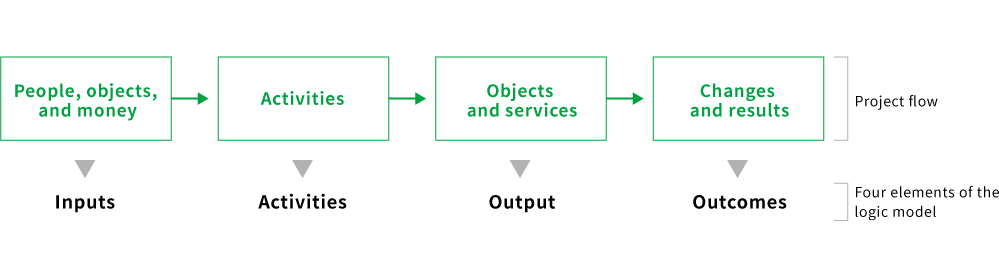
The logic model visualizes the theoretical cause-and-effect relationships from business activities to outputs and outcomes.
Glossary
Impact Evaluation Process
Five dimensions of Impact
Impact dimensions
Impact questions each dimension seeks to answer
What
What tells us what outcome the enterprise is contributing to, whether it is positive or negative, and how important the outcome is to stakeholders.
Who
Who tells us which stakeholders are experiencing the outcome and how underserved they are in relation to the outcome.
How much
How Much tells us how many stakeholders experienced the outcome, what degree of change they experienced, and how long they experienced the outcome for.
Contribution
Contribution tells us whether an enterprise’s and/or investor’s efforts resulted in outcomes that were likely better than what would have occurred otherwise.
Risk
Risk tells us the likelihood that impact will be different than expected.
“Why Impact Evaluation” is Needed
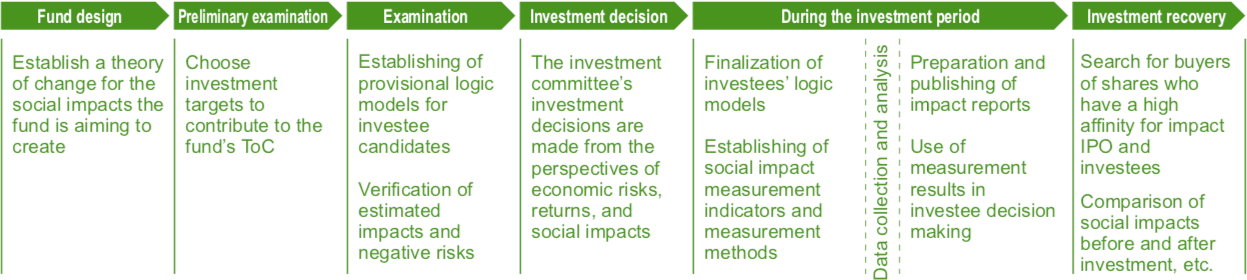
Measurement process for this fund

Constituent elements of logic model following the flow of the project
Case studies
Five strategic themes for accomplishing our mission
Impact bonds (SIB)


